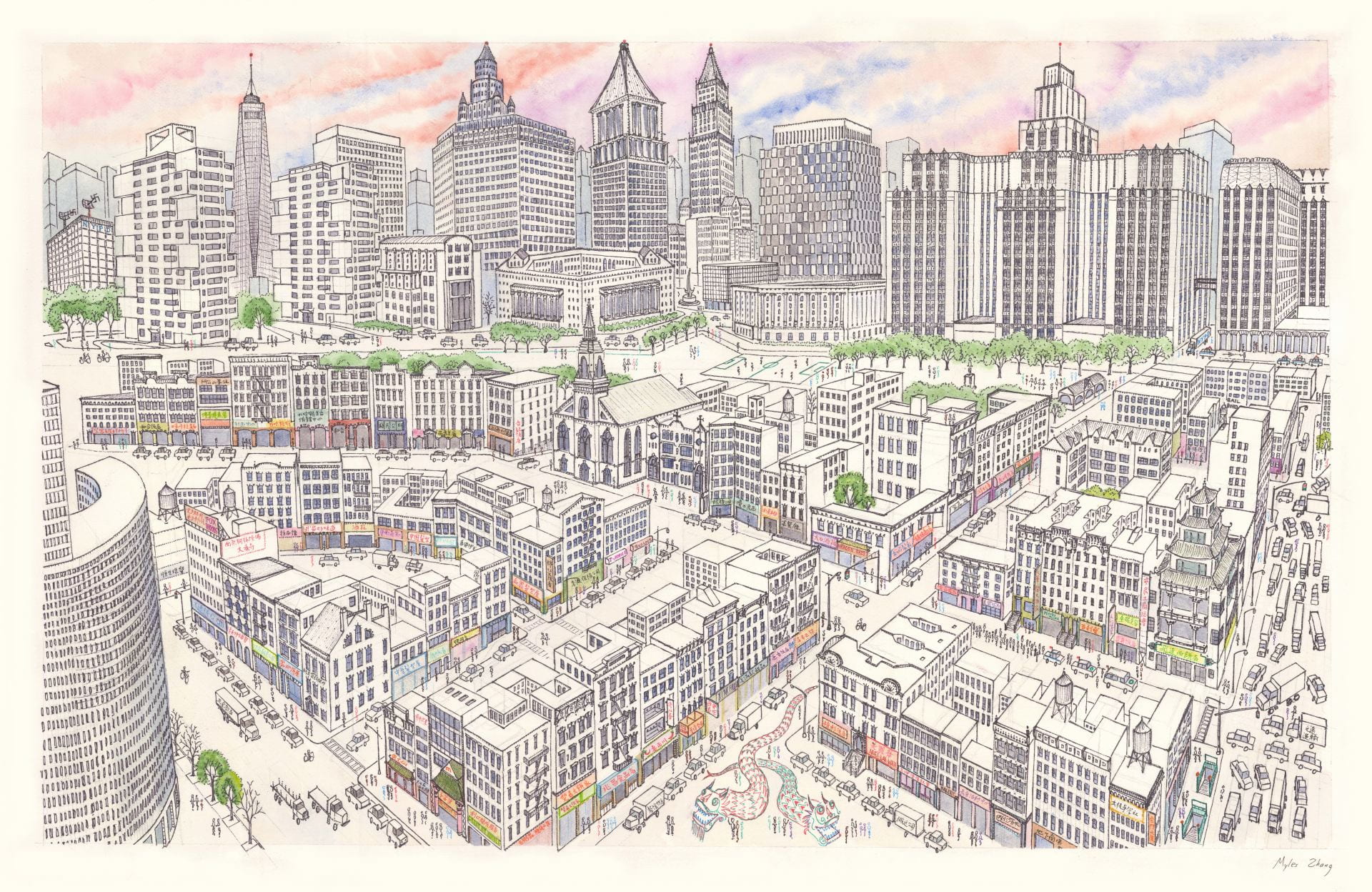
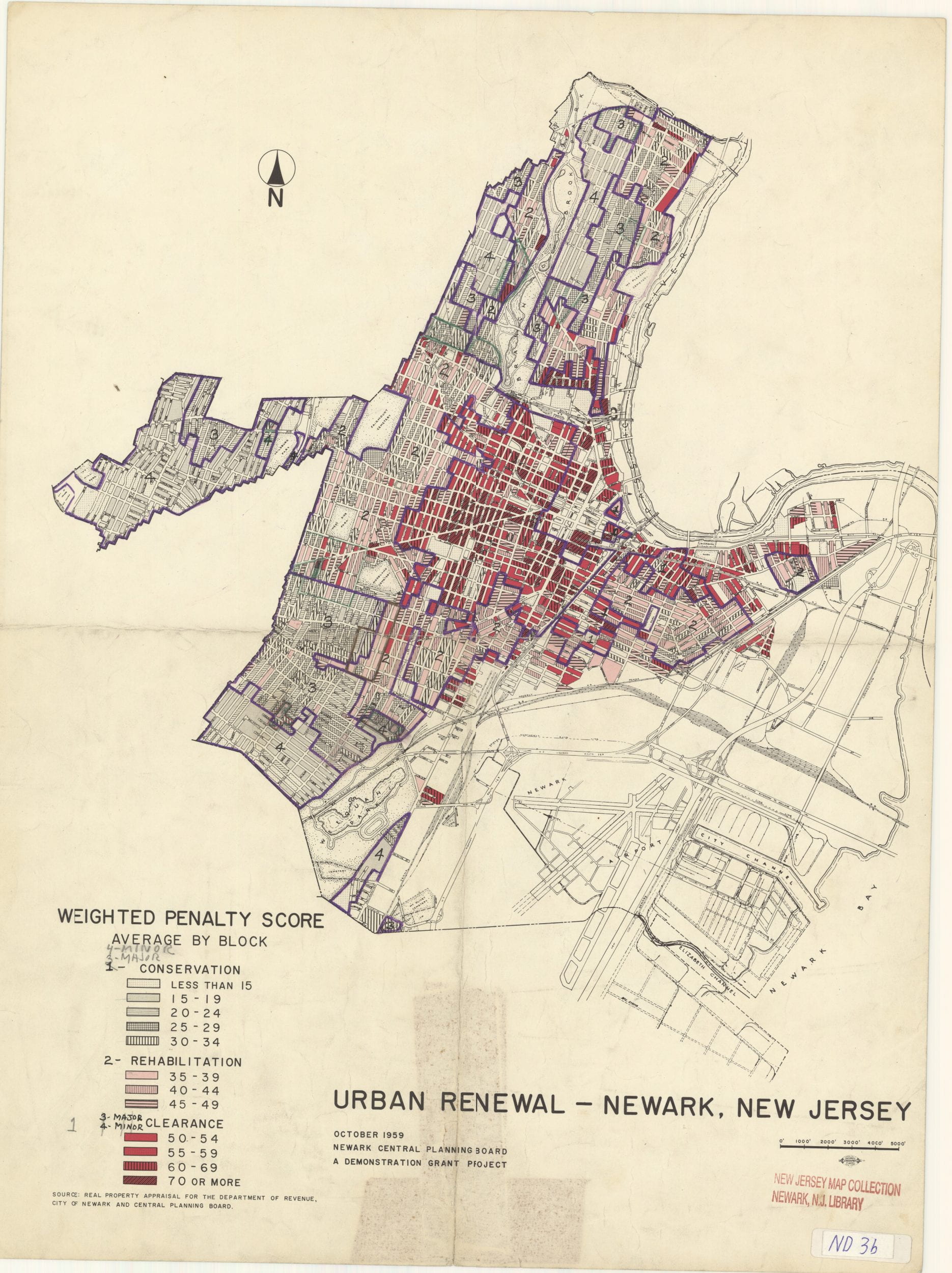
No comments

Myles Zhang
View publications by category:
200+ Posts
architecture of fear British history building construction car culture cathedral construction sequence Chinatown collection data visualization Detroit dissertation project drawing Eastern State Penitentiary essay film historical GIS historic preservation history of technology medieval history models Newark Newark art Newark history New York City NYC art NYC history NYC photography panopticon pastel photo-essay photography planning politics pop-up cities prison history program application essays proposals for architecture protest public speaking rail travel ruins sounds of the city time-lapse cartography walking watercolor waterfront